In the ever-evolving landscape of the United States, the financial journey of young adults is taking a distinct turn from that of their parents. A recent report from the Pew Research Center sheds light on the challenges faced by the younger generation, highlighting their delayed milestones, increased reliance on parental support, and the mounting debt burden they carry. This article delves into the key findings of the report, exploring the factors contributing to the financial dynamics of young adults in the U.S.
Financial Dependency: A Majority Struggle

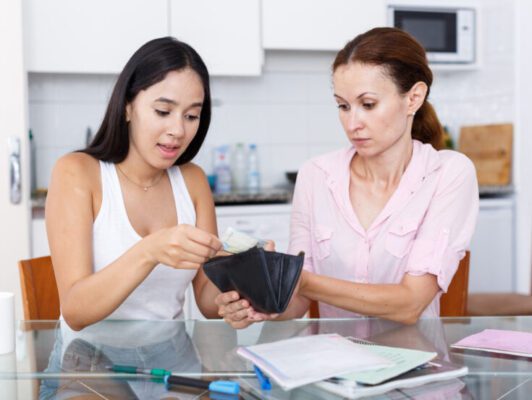
The Pew Research Center’s study reveals a stark reality — a significant majority of young adults in the U.S. acknowledge a level of financial dependency on their parents. Surprisingly, only 45% of individuals aged 18 to 34 consider themselves completely financially independent. The younger cohort, particularly those aged 18 to 24, is most likely to lean on their parents for financial support, with over half relying on assistance for basic household expenses.
Debt Dilemma: A New Generational Challenge
Beyond financial dependence, the report highlights the burden of debt carried by young adults, a challenge not experienced to the same extent by their parents. The analysis indicates that today’s young adults, straddling the Gen Z and millennial generations, are more likely to pursue higher education. While this trend brings the potential for higher lifetime earnings, it also brings a downside — an increase in student loan debt. Approximately 43% of individuals aged 25 to 29 carry student debt today, a significant rise from 28% in 1993.
Homeownership, a traditional marker of financial stability, also comes with a heavier burden for young adults. The study reveals that those aged 29 to 34 who own homes have approximately $190,000 in mortgage debt today, compared to $120,000 in 1993 when adjusted for inflation.
Also Read : Florida’s Social Media Age Restriction Bill Balancing Protection and Rights
Living Arrangements: The Rise of Multigenerational Living
Mounting debt and financial challenges are reshaping living arrangements for young adults. Pew suggests that the cost of housing and rent plays a pivotal role in this shift. Currently, about 57% of individuals aged 18 to 24 are living with their parents, up from 53% in 1993. The study suggests that the societal stigma associated with staying at home has diminished, making it a more acceptable arrangement.
Kim Parker, director of social trends at Pew, emphasizes the impact of housing costs, stating, “The arrangement a lot of adults have with living with parents has become much more acceptable than in prior generations.”
Delayed Milestones: Marriage and Parenthood
Financial challenges are not only influencing living arrangements but also delaying key life milestones for young adults. In 1993, 63% of individuals aged 30 to 34 were married; today, that figure has dropped to 51%. The decline is even more pronounced in parenthood, with 60% of the same age group having at least one child in 1993, compared to a mere 27% today.
Parker notes, “It’s a relatively big change over a short period of time. It all suggests a kind of delay.” While the financial strain of raising children is undoubtedly a contributing factor, cultural shifts also play a role, as evidenced by another Pew study indicating a growing share of Americans not expecting to have children.
The financial landscape for young adults in the U.S. is undergoing a profound transformation, marked by increased dependence on parental support, mounting debt, and delayed life milestones. While these challenges paint a complex picture, there’s a prevailing sense of optimism among young adults. Despite their current financial struggles, three out of four individuals dependent on their parents believe they will eventually achieve financial independence.
As we navigate these changing dynamics, it’s crucial to understand the interplay between economic factors, cultural shifts, and individual aspirations. Acknowledging the challenges is the first step toward crafting policies and societal norms that support the evolving financial journeys of the younger generation.