Understanding the March Inflation Surge
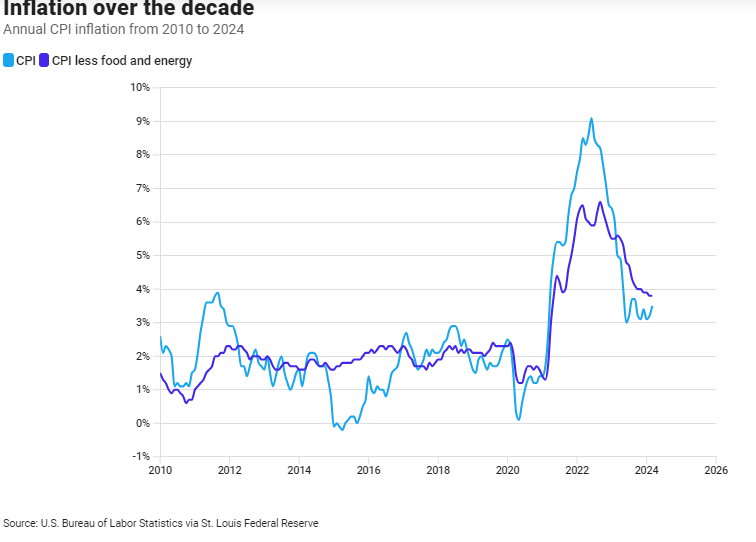
Inflation, the persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services, has been a concerning economic trend in recent months, with March marking the third consecutive month of acceleration. This surge in inflation has profound implications for consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike. The latest data from the Labor Department reveals that inflation accelerated by 0.4% in March from the previous month, surpassing expectations and raising alarms about the sustained high prices experienced by millions of Americans.
Persistent Price Pressures
The consumer price index (CPI), a crucial metric for gauging inflation, provides insights into the cost of everyday essentials such as gasoline, groceries, and rent. In March, the CPI surged by 3.5% compared to the same period last year, a significant increase from the 3.2% recorded in February. This acceleration not only outpaced previous forecasts but also underscores the persistent nature of price pressures within the economy.
Exceeding Projections
Economists had anticipated a more moderate increase in inflation, with projections of a 0.3% monthly rise and a 3.2% year-on-year gain. However, the actual figures surpassed these expectations, signaling a more significant challenge in taming inflationary forces. Additionally, core prices, which exclude the volatile components of food and energy, also saw a substantial uptick of 0.4% in March, mirroring the trends observed in January and February. This consistent rise in core prices contributed to an annual gain of 3.8%, further surpassing estimates and adding to concerns about inflationary pressures persisting across various sectors of the economy.
Implications for Policy and Economic Outlook
The unexpected acceleration in inflation presents a complex set of challenges for policymakers, particularly the Federal Reserve. Inflation exceeding projections not only underscores the magnitude of price pressures but also complicates monetary policy decisions. With inflation running above the Federal Reserve’s target of 2%, the central bank faces the dilemma of balancing its dual mandate of price stability and full employment.
Delayed Rate Cuts
The March inflation figures are likely to postpone any imminent interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. Historically, central banks have employed interest rate adjustments as a tool to mitigate inflationary pressures. However, with inflation rates consistently surpassing expectations, the Federal Reserve may opt for a more cautious approach to avoid exacerbating inflationary trends.
Consumer and Business Impact
For consumers, the sustained high prices translate into increased costs of living, potentially eroding purchasing power and limiting discretionary spending. Moreover, businesses grapple with higher input costs, which may ultimately be passed on to consumers, further fueling inflationary pressures. This scenario underscores the interconnectedness of inflation dynamics and its widespread impact on economic stakeholders.
Conclusion
The March inflation data underscores the persistent nature of price pressures within the economy, with inflation accelerating for the third consecutive month. Exceeding projections, these figures pose challenges for policymakers and economic stakeholders alike. As the Federal Reserve navigates the delicate balance between addressing inflationary pressures and supporting economic recovery, consumers and businesses must brace themselves for continued uncertainty in the inflation landscape. Addressing these challenges will require a comprehensive approach encompassing monetary policy, fiscal measures, and structural reforms to safeguard economic stability and ensure sustainable growth.